

If you do have RA, you need an individually developed treatment plan 2. See our right care for RA fact sheet. You can check out the approaching pain management module: this gives you some practical tips for managing mood and access to some online training modules. You may also find clinical psychology helpful especially if you experience low mood, persistent pain or have difficulties coping with your RA. The podiatrist can advise you on appropriate footwear and supportive insoles to relieve foot pain and prevent or support foot deformities. The occupational therapist can provide splints for inflamed or deformed hand joints and can advise you about aids to help you to function better as well as modifications at work and at home. The physiotherapist with skills in RA management can advise you about an appropriate exercise programme and activities to maintain joint function and muscle strength and to help manage pain. The rheumatology nurse can provide emotional support as well as giving you information on your disease, medications and RA support groups. Nurses and physiotherapists play a large role in helping people with RA manage their disease symptoms and maintain participation in daily work, home and recreational activities. He or she may also recommend visits to relevant health professionals (such as a rheumatology nurse, physiotherapist, occupational therapist, and podiatrist). The rheumatologist will ask you about your symptoms, perform a thorough examination and request further investigations in order to make decisions about your diagnosis, management and the role of medications. Based on these results, you may be referred to a specialist called a rheumatologist who will help guide you regarding further RA management.ĭiagnosing RA early and starting the right treatment at the right time will result in a better outcome. Your doctor will arrange blood tests and possibly x-rays and other imaging. If you suspect that you may have RA, we recommend you consult your doctor to discuss the potential for further investigations to diagnose RA and guide your management. You might find the pacing and goal setting or approaching pain management modules helpful. If you are in pain and feeling anxious, depressed, and not sleeping well, this feeling of fatigue can be very pronounced. Sometimes trying to exercise in the hope you’ll improve may make the feeling worse and this can be disheartening.

You may find that resting more does not help this feeling.
Ra more info skin#

RA is the most common auto-immune disease in Australia, affecting about 2% of the Australian population 1.
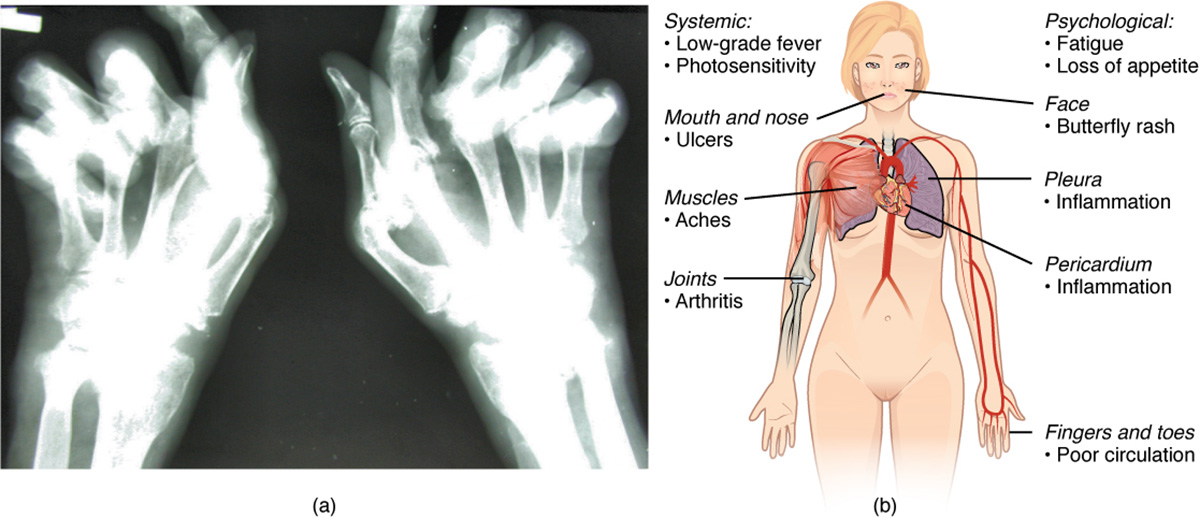
Other joints such as shoulders, knees and neck can also be affected. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease that affects primarily the joints, typically the smaller joints in the hands and feet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
